Covalent Bonding
and Atomic Shapes
Covalent bond
A
covalent bond is between two non-metals and involves the ‘sharing of electrons’.
Definition: A shared pair of electrons.
There is a force of attraction between the bonding pair of electrons and the
nuclei of the atoms.
Covalent
properties:
·
Low melting point due to the weak inter-molecular forces
(except for diamond and silicon);
·
Most dissolve better in non-polar solvents e.g. cyclohexane;
·
Few dissolve in H2O (there are some exceptions
e.g. Ammonia forms NH4OH);
·
They don’t conduct electricity (except graphite which
has a free electron).
Low
melting/boiling points in simple covalent compounds:
This
is because although the bonds between atoms is strong the inter-molecular forces
are weak. It is these forces that break when the compound is heated.
Covalent
compound are represented by either dot and cross diagrams or H – O – H
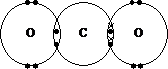 Examples: CO2
Examples: CO2
or O = C = O
Dative covalent bond
A
Dative covalent bond is when a lone pair of electrons is shared with an electron deficient compound (a compound
that has not reached the nearest noble gas structure e.g. BF3).
 BF3
BF3
Definition
of Dative covalent bond
A covalent bond where both the bonding electrons are supplied by one atom.
Whilst
the F atoms have reached a noble gas structure the B atoms still require another
two electrons. This means BF3 could form a further bond.

E.g.
NH3 bonds with BF3
H F
| |
H – N -> B – F
| |
H F
5 Molecular Shapes
In
the exam you may be asked to describe and draw the shapes of molecules. It is
therefore vital you can draw the molecules and remember the bond angles and
molecular names.
Electron repulsion theory
Pairs of electrons repel each other and therefore arrange themselves as far apart as possible. The repulsion between lone pairs is greater than that between bonding pairs.
For the Exam:
·
You must mention
the number of lone pairs of electrons in the molecules.
·
You must also
mention the number of bonding pairs of electrons.
·
And you must
mention that repulsion between lone pairs in greater than that of bonding pairs.
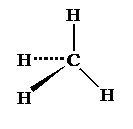 Molecular shapes
Molecular shapes
4
bonding pairs
Name:
Tetrahedral
Bond
angle: 109.5°
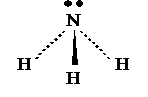
3
bonding pairs, 1 lone pairs
Name:
Pyramidal
Bond
angle: 107°
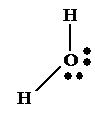
2
bonding pairs, 2 lone pairs
Name:
Non-linear (Angular)
Bond
angle: 104.5°
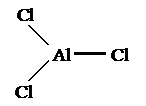
3
bonding pairs 0 lone pairs
Name:
Triginal planer
Bond
angle: 120°
![]() 4 bonding pairs 0 lone pairs
4 bonding pairs 0 lone pairs
Name:
Linear
Bond
angle: 180°
Note:
When drawing molecular shapes in the exam remember to include any double or
triple bonds!
