Scalar & Vectors
Definition of a scalar: A quantity with size (magnitude)
only.
Examples: speed, distance, time, mass, volume, work
done, pressure, energy, power and density.
Definition of a vector: A quantity with size (magnitude)
and direction.
Examples: displacement, velocity, force, weight, gravitational
field strength and acceleration.
Displacement is the vector alternative for distance and is defined as distance moved in a particular direction. Velocity in turn is the vector alternative for speed and is defined as speed in a stated direction.
Take the following example:
Tom and Amy are taking a walk in the park. They follow the winding pathway and walk a total of 500m. Their distance is 500m, however their displacement is only be 300m west to east.
Path taken
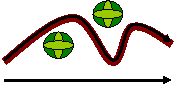 |
Distance = 500m
Displacement = 300m from west to east
Note that all vector quantities can be positive or
negative depended on direction.
Some fundamental equations
Speed = Distance
Time
Where Speed (m/s or ms-1)
Distance (m)
Time (s)
Acceleration = Change in Velocity
Time Taken
Where Acceleration (ms-2)
Change in Velocity (ms-1)
Time Taken (s)
